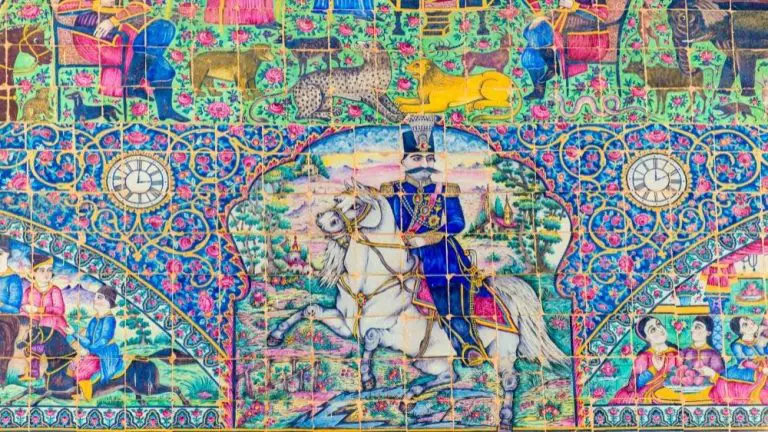
What is Folk Art? (Explained)
Folk Art is everywhere around us. It is unaffected by revolutions or academic theories. It includes work created by indigenous people, peasants, and other low-wage workers.
Folk art, unlike fine art, is largely functional and decorative rather than solely attractive. It is distinguished by a naive style that rejects established proportion and perspective principles.
Folk Art History

(This article may contain affiliate links and I may earn a commission if you make a purchase)
“Folk art” is a word coined by white Christian, well-educated urbanites in the nineteenth century to characterize the charming arts and crafts of rural civilizations. Historically, this form of artwork has been classified as either utilitarian or decorative rather than just beautiful. Folk art, which is created by artistically minded individuals from different cultures around the world, directly reflects a society’s ideals.
It refers to artwork that is created by people with artistic talent who use their community’s actual cultural identity rather than a distinct aesthetic one. Folk artists learn most of their talents and skills through apprenticeships in informal social networks. Some, on the other hand, may acquire academic training.
Folk art in general:
- Can be decorative or practical/efficient
- Is handcrafted; it may have both handmade and new, artificial, or recycled components.
- Could be made for use within a community of practice or for sale as a source of money and empowerment
- Can be taught academically or informally, and it can also be self-taught
- Dance, singing, poetry, and foodways are examples of intangible forms of expressive culture.
- Is traditional; it represents cultural aesthetics and social problems that are shared. Traditional folk art may vary through time and may incorporate innovations in tradition, as traditions are dynamic.
- Is for, by, and about the people; everyone, regardless of class, rank, culture, community, race, gender, or religion.
Characteristics of Folk Art

- As we already mentioned, folk art is distinguished by the fact that it is unaffected by academic or fine art movements.
It does not always contain artistic customers’ purchases of “high-class art” or “artwork” handled by a professional artist. However, numerous folk artists in the U. S. in the 18th and 19th centuries, notably itinerant portrait painters, made a livelihood from their painting work. Furthermore, some of them have left a substantial collection of artwork behind. - Among the names that overlap with folk art are naive art, primitive art, pop art, outsider art, traditional art, popular art, tribal art, tramp art “wandering art,” and “self-taught” art.
- Folk art is an art that has emerged from a folk heritage and has a functional and aesthetic element. It is common people’s work, intended for a limited audience, and lacking in artistic pretensions. It’s mostly practical and handcrafted for personal, limited, or collective use. Paintings are frequently used to decorate trunks, clocks, and inside or external walls.
- It shows cultural identity by conveying shared community values and artistic taste. It also has a variety of utilitarian and decorative media such as fabrics, wood, papers, clay, metal, and many other things. When traditional materials are no longer available, new resources are frequently substituted, resulting in contemporary versions of traditional folk art forms.
- Folk art portrays the traditional art forms of a wide range of community groups — ethnic, tribal, religious, commercial, regional, age, or gender-based — who identify with one another and with society as a whole.
- Quilting, ornate picture frame, and decoy carving are only some of the folk art traditions that are still practiced, and new ones are always developing.
Antique Folk Art

Such folk art refers to artifacts created by “country folk,” some of which were created to be admired, but many of which were practical products with a decorative feature such as a carved heart. Taking an ordinary item and making it into something more unique.
Contemporary Folk Art
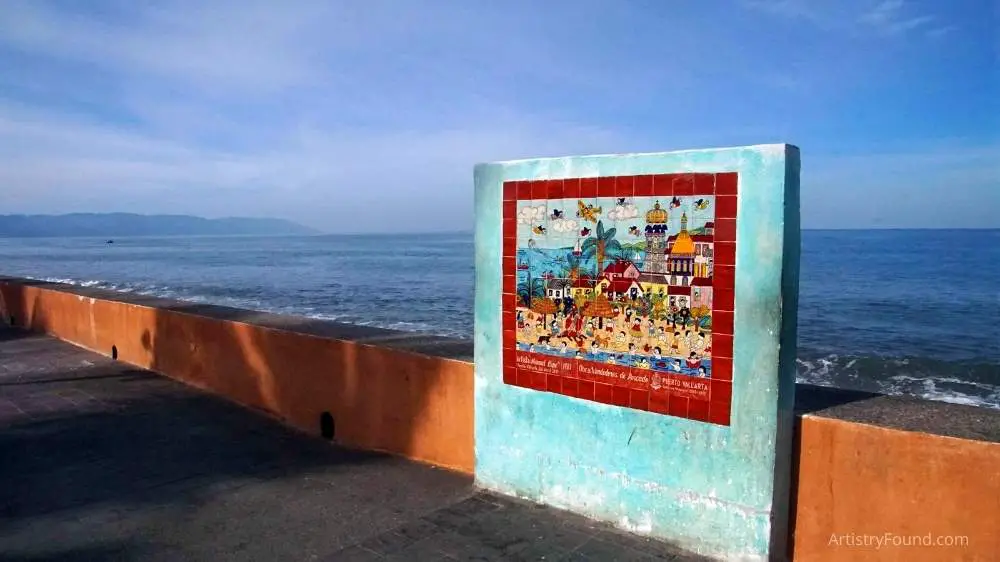

Many folk art traditions, such as quilting, ornate picture frame, and decoy carving, are still alive and well, while new forms develop on a regular basis. Because their work is generally generated in isolation or in small towns across the country, contemporary folk artists are frequently self-taught.
Folk Arts have influenced mainstream art, and these artworks have influenced many artists too. For example, African tribal sculptures and masks influenced Pablo Picasso, while traditional Russian popular prints known as luboks inspired Natalia Goncharova and others.
Why is Folk Art Important?
Here is why folk art is important:
- Rituals, festivity, and community are all incorporated into folk art. These are critical for passing down our ethnic groups’ cultural values from generation to generation. The showcasing and sharing of folk arts in the community adds to the diversity of our neighborhoods.
- It is critical to know that traditional art is not a rigid form that does not develop with time. It is a creative process, much like any other art form; however, the ideas come from history, culture, and community practice.
- It can shift and grow as the artist digs deeper into their roots and the communities where they dwell. Immigrants make up a large portion of our folk artists and teachers. The protection and preservation of our community’s tradition-bearers, instructors, and artists are critical.
- The social and economic benefit of knowledge transfer is crucial for both minority and mainstream social groups within a state, and it is equally vital for developing and developed countries.
- Self-taught artists’ work contributes to the expression of cultural identity by articulating shared community values.
Since they are not well-known or understood, traditional folk artists are frequently disregarded and dismissed in the funding sector. If we could better grasp the cultural foundations, customs, and arts of our immigrant populations, our world and society would be a better place.
Folk Artists and Their Works
Ammi Phillips

Ammi Phillips, born in Colebrook, Connecticut, was an early American folk art painter.
Phillips was an untrained artist who learned to paint by examining imported prints. He worked in Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New York and was known as the Border Limner and the Kent Limner.
Famous Work: Girl in red dress with cat and dog
Henry Darger

Henry Darger is a great storyteller whose artworks were motivated by his personal mental health and upbringing.
He is regarded as one of the great “outsider painters.” The story of the Vivian girls is undoubtedly Darger’s best and most acclaimed work. This specific work, which is thought to date back to 1909, is made up of twelve volumes. The plot of this series unfolds in a way that is now widely recognized as strongly influenced by the Civil War.
Leonard Knight

Leonard Knight had no professional artistic training and, until very late in life, refused to be labeled an artist. His naive approaches, primitive materials, humorous style of painting, and haphazard construction methods contributed to American Folk Art traditions.
This, paired with his rebellious and destitute living on the margins, cemented his reputation as one of our great outsider artists, paving the way for future artists operating on the margins of the established art world.
Known For – Salvation Mountain
Anna Mary Robertson Moses

Also known as Grandma Moses, she had no official training as an outsider artist with “folk” and “naive” tendencies; she was an unusually inventive figure who worked in isolation.
Grandma Moses’ paintings depict everyday agricultural operations such as “sugaring off” (producing maple syrup), shearing and bathing sheep, and making soap and butter, to name a few. These actions are depicted in her paintings as highly creative undertakings in and of themselves.
In addition, the paintings frequently have a three-dimensional appearance that harkens back to the artist’s previous work as a yarn embroiderer.
Jamini Roy

Jamini Roy was an Indian painter who started off as a commissioned portrait artist. He was inspired by the Kalighat Pat (Kalighat painting), a type of art with broad sweeping brushstrokes, and looked to contemporary folk and tribal art for inspiration.
Roy quickly established a new style based on Bengali folk traditions, with the goal of capturing the essence of simplicity reflected in the lives of indigenous peoples, making art accessible to a wider audience, and giving Indian art its own identity via his work.
Famous work – Three Pujarins
How to Preserve Folk Art?
Below are ways to preserve folk art:
Seminars to Raise Awareness
The majority of individuals follow the current trends while rejecting all traditions. Only a small percentage of the older generation has a solid understanding of diverse art and cultural genres.
So that no art form goes extinct, the youth of today must be persuaded of the importance of capturing such vast amounts of information from their elders.
Education
In today’s global culture, cultural heritage appreciation should be expressed through an integrated education method. Education should be supported as a means of ensuring the long-term preservation of cultural assets. It is a method of preserving both tangible and intangible cultural heritage.
Workshops
Workshops are locations where you can let go of all your inhibitions. They’re fantastic places for people to interact, learn, and grow. They are held under the supervision of experts from various fields. The interactive platform allows attendees to contribute their knowledge and learn new things at the same time.
Fairs and Exhibitions

Exhibitions and fairs are the most effective means of preserving art forms such as painting and sculpture. People can view a variety of traditional fine art pieces that have been meticulously made. Shows like these encourage children to learn traditional art forms.
Live Performances
Live performance has an effect that no seminar or awareness workshop can match. Many people have the opportunity to see and study old art styles. It is fairly typical to witness someone who has never heard of a certain art form become a fan after seeing a live performance by a talented performer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Indian folk art or traditional art?
Pottery, sketching, metalwork, paperwork, weaving, and designing things like jewelry and toys are examples of Indian folk and traditional art forms. These aren’t just decorative items; they have deep cultural, religious, and regional significance in India.
What is the difference between traditional art and folk art?
Folk and traditional arts are deeply based in and reflective of a community’s cultural life. They cover a wide range of expressive culture that is linked to folklore and cultural history. Objects that have historically been produced and used within a traditional community are considered tangible folk art.
How is Contemporary art different from traditional art?
The phrase “contemporary art” refers to art made in the current era. Folk art is a type of traditional art that includes art created by indigenous people, peasants, and other laborers. They reflect contemporary ideas and viewpoints that are vulnerable to societal change.
What is the difference between traditional and folk arts?
Folk and traditional arts are those that are developed as part of the cultural life of the community whose people share a shared ethnic history, cultural beliefs, dialect, religion, occupation, or geographical area.
What is Korean folk art?
Minhwa is a term used to describe Korean folk art created primarily by nomadic or untrained artists who imitate contemporary fine art styles for the sake of everyday utility or decoration. Yanagi Muneyoshi coined the term “minhwa.”
Why is it critical to preserve art?
Historical objects must be preserved for future generations to remember and respect their contributions. The historical story is preserved for future generations as long as an artifact is conserved in its existing condition.
What can we do to preserve art?
For artwork, experts recommend a humidity level of 55 percent. It’s best to keep your artwork in a cool, dry, and dark environment: The best approach to protecting your artwork from the negative consequences of sunshine and humidity is to keep it cool, dry, and dark. It is actually incredibly effective when it comes to safeguarding unframed artwork.
What is Folk Art – Conclusion
That’s it! I hope you now have a better understanding of folk art and how to revive it!